What is Zinga?
ZINGA is a zinc-rich coating containing 96% zinc in its dry film, offering full cathodic protection rather than acting as a paint. It meets ISO 3549 for zinc purity (99.995%) and ASTM A780 for hot-dip galvanization repair.
Unlike traditional paints, ZINGA provides both Active and Passive protection while being as easy to apply as paint. It can also be overcoated for added protection or aesthetics.
Originally developed at Ghent University, Belgium, in the 1970s, ZINGA has been used globally for corrosion protection. Unlike passive coatings, it bonds with metal rather than just forming a barrier. It also has an unlimited pot-life, never skins over, or becomes tacky like paint.
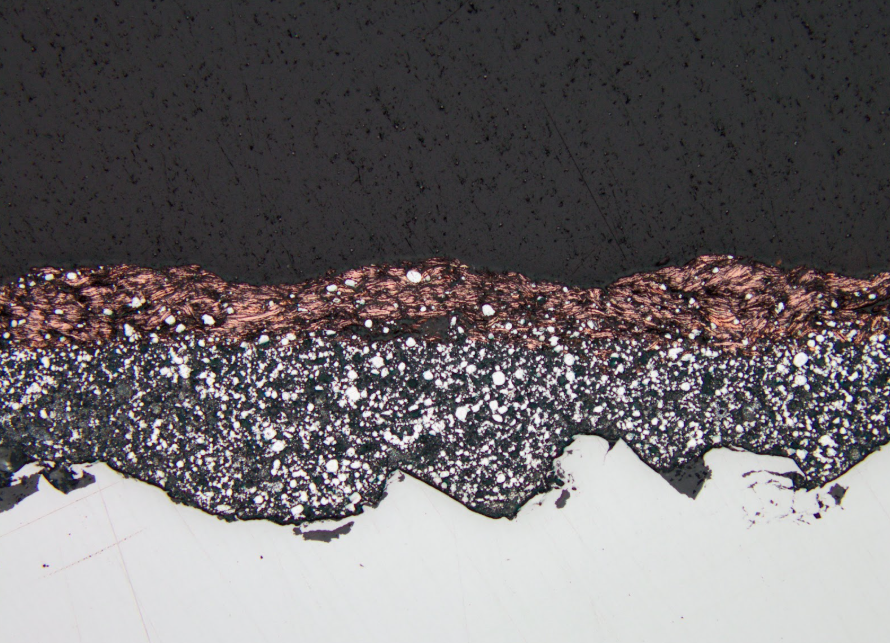
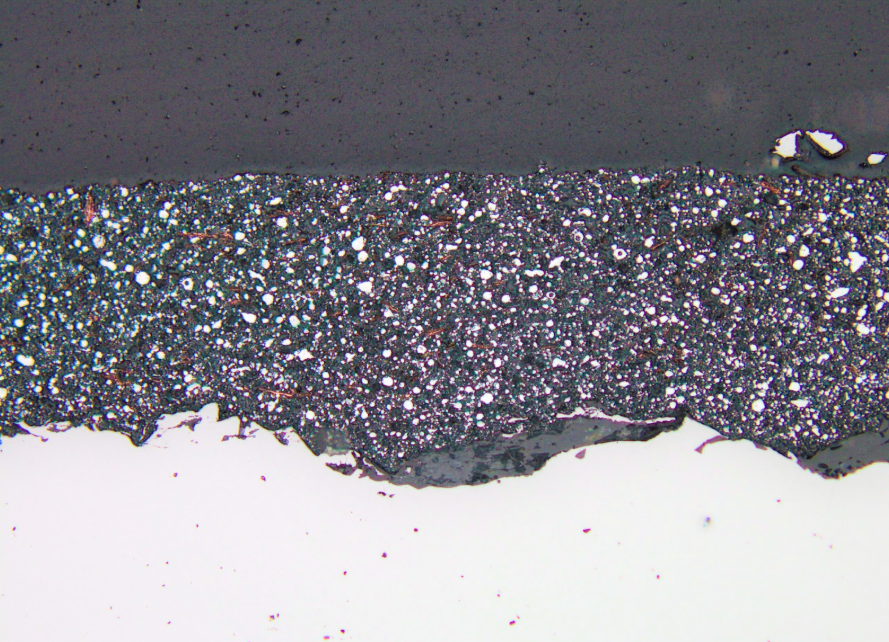
Microscopic Zinga layer
How Does it Work?
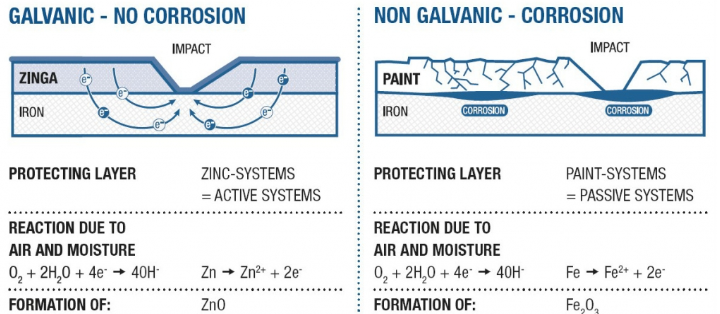
When two metals contact in the presence of an electrolyte (e.g., water), a galvanic reaction occurs, where the less noble metal (zinc) corrodes to protect the more noble metal (steel). This process, called cathodic protection, prevents steel corrosion, even if the zinc layer is slightly damaged. Common methods include hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) and zinc thermal spraying, which maintain a constant sacrificial rate of zinc.
ZINGA reduces this sacrificial rate after oxidation fills its natural porosity with zinc salts. Its organic binder protects zinc particles while maintaining conductivity, creating a lower rate of zinc loss than HDG. The zinc in ZINGA acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding at a much slower rate than expected. If damaged, the steel forms zinc corrosion products instead of rust, protecting exposed metal up to 3–5 mm beyond the coating. Similar to zinc anodes on boat hulls, ZINGA functions as a liquid anode, offering superior long-term protection.
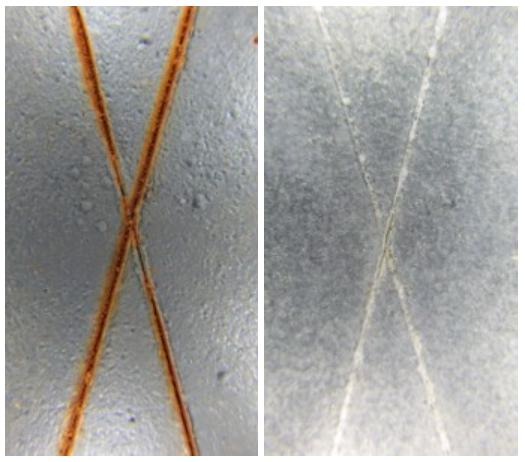

Containing 96% pure zinc, ZINGA ensures strong cathodic protection by maximizing zinc contact with the steel surface. Unlike passive coatings like paint, which act as barriers that corrode once breached, ZINGA’s zinc oxide layer continuously self-renews, maintaining protection over time.

The zinc in Zinga becomes the sacrificial anode in relation to the steel but it corrodes at a much slower rate than would otherwise be expected
Extract from B.N.F. Fulmer report of JJB Ward, Oxfordshire, Jan ’92
How Can it Be Used?
Standalone System
ZINGA offers protection comparable to galvanizing without topcoats. It can be re-coated anytime with minimal preparation, making it ideal for large structures, delicate designs, or when a high-quality finish is needed. For optimal protection, apply two layers of 60–90 µm DFT.
Primer in Duplex & Triplex Systems
As a primer, ZINGA extends system lifespan by preventing under-creep and blistering. It preserves zinc thickness until the topcoat is breached. Apply one layer of 60–80 µm DFT for duplex/triplex systems.
Shop Primer
At 30–40 µm DFT, ZINGA can be used as a shop primer, allowing welding and bending without requiring re-blasting before overcoating.
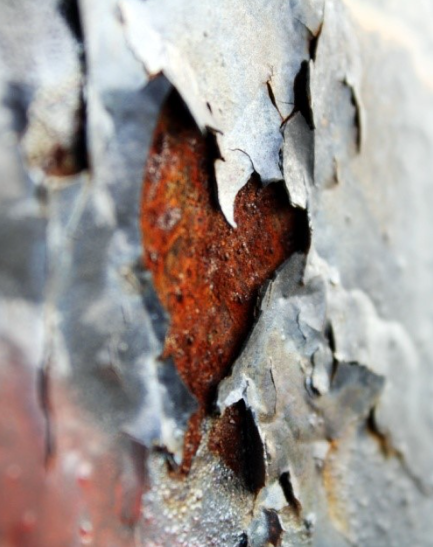
Repair for Galvanized or Metal-Sprayed Structures
ZINGA seamlessly restores worn or damaged galvanization, acting as a “re-charge” to extend asset lifespan. Surface preparation involves decontamination and salt removal.
Rebar Protection
Used globally in construction, ZINGA protects steel rebars without reducing pull-out strength. Studies confirm it provides twice the corrosion resistance of standard paints.
Characteristics & Advantages
Simple On-Site Application
ZINGA can be applied using a brush, roller, or spray gun in temperatures from -15°C to 40°C, with up to 95% humidity. Unlike hot-dip galvanizing, it doesn’t deform steel structures.
Fast Drying & Cost-Efficient
Touch dry in 10 minutes at 20°C, ZINGA allows recoating in 1–2 hours and topcoats in 6–24 hours, reducing downtime and labor costs.
Durable & Flexible
Unlike paint, ZINGA doesn’t peel or crack. Its porous structure maintains electrical conductivity, ensuring long-term cathodic protection, even when bent or impacted.
Recharging Capability
ZINGA can be recoated anytime without peeling. It integrates with existing layers, requiring only minimal surface cleaning before reapplication.
Topcoat Compatibility
ZINGA extends duplex system longevity by preventing undercoat corrosion. It must be top-coated using compatible primers and sealers to avoid chemical reactions.
Application
Application Methods
ZINGA can be applied using a paintbrush, short-fiber roller (not for the first coat), conventional, or airless spray gun. It must be thinned only with Zingasolv and thoroughly mixed before use. It applies in -15°C to +40°C with up to 95% humidity, ensuring minimal weather-related delays.
Surface Preparation
Proper surface cleaning is crucial for adhesion and cathodic protection. The steel must be free of dirt, oil, grease, salts, and mill scale, removed via steam, detergent, or solvent cleaning. A rough profile (Rz 50–70 µm) is required, achieved by grit blasting, slurry blasting (SA 2.5), or UHP washing.

Dilution & Spraying
Brush/Roller: 3-5% dilution for a smooth finish.
Conventional Spray: 10-20% dilution for better circulation.
Airless Spray: 5-7% dilution for an even coat.


ZINGA can be applied to old hot-dipped or Zinganised surfaces using a brush, roller, conventional, or airless spray. However, the first layer should never be applied by roller as it won’t penetrate the steel’s roughness profile. For proper adhesion, the first layer should be slightly more diluted than standard. Brush application requires 5-10% Zingasolv dilution for a smooth finish and better penetration. Avoid heavy brush marks to prevent uneven coating, pinholes, or spot rusting.
Recharging & Overcoating
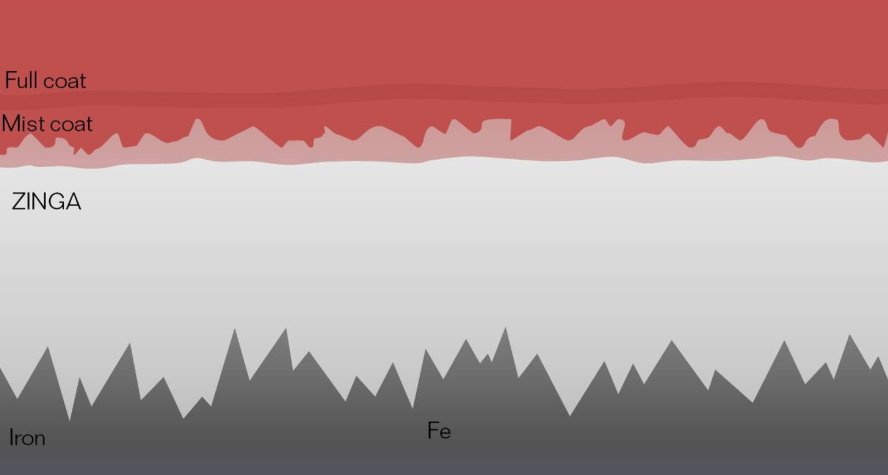
ZINGA can be recoated anytime without peeling—just remove zinc salts before application. When overcoating with a topcoat, a mist/full coat technique ensures proper adhesion and prevents bubbling. Avoid alkyd and water-based paints, as they may react with the zinc.